Last updated on September 27th, 2024
Here’s an overview:
Introduction to Pugs and Diabetes
Identifying Diabetes Signs in Pugs
Diagnosing Diabetes in Your Pug: What to Expect
Creating a Treatment Plan with Your Veterinarian
Administering Insulin: What Are Tips and Techniques
The Role of Diet in Managing Pug Diabetes
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels: Tools and Techniques
Out of Many Ways To Manage This Condition: Scheduled Return And Monitor
Support Systems: Family, Vet and Pug Communities
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Success Stories: The Experiences of the Administrators of Diabetes in Pugs
Further Development Directions in Canine Diabetes Management
Introduction to Managing Pug and Diabetes
Managing Pug and the condition of pug diabetes is considered chronic owing to the unregulated state of the blood sugar in the pugs’ bodies. There are two main types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: The pancreas does not produce enough insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The body’s cells become immunized with insulin.
The following abnormities may be witnessed:
- Excessive thirst
- Increased frequency of urination
- Crossing realities and living whilst one is low on physical mass but has an average rate of consuming food
- Low energy levels
Pugs are carried away with the genetics of making them more vulnerable to obesity, therefore making them vulnerable to the development of diabetes. Detection timely before the condition gets out of hand is essential.
Identifying Diabetes Signs in Pugs
Knowing the symptoms of diabetes in Pugs is important so that the disease can be diagnosed and treated in the earliest stages possible. It is the owners of the Pugs who should be on the lookout for their pets and the following signs should be noted:
- Increase in Thirst: Pugs with diabetes mellitus may increase the amount of water they drink more than they normally do.
- Increase in Frequency of Urination: An increase in urination may be due to the concentration of high blood glucose levels.
- Getting cloudy eyes: This can also be a symptom mets of diabetic cataracts.
- Increase in Hunger Level: Increased consumption without increased weight can be explained using these signs.
If these symptoms are observed the owners should see a veterinarian.
Diagnosing Diabetes in Your Pug: What to Expect
Concerning pug populations it is important to examine how a veterinarian usually proceeds to diagnose diabetes in a pug.
- Medical History Review: Considers up to the symptoms for increased thirst and excess of urination.
- Physical Examination: Look out for lethargy, weight loss or cataracts.
- Blood Tests: Blood glucose levels are tested.
- Urinalysis: Presence of glucose and ketones in the urine.
- Additional Blood Work: Evaluates the general condition of the pet and how the organs are functioning.
- Fructosamine Test: Measures how high the average blood glucose was during the past few weeks.
There are several factors responsible for this wide variety of management. Pugs can be managed successfully if diabetes is diagnosed early.
Creating a Treatment Plan with Your Veterinarian
Formulating a detailed management strategy includes the participation of a treating veterinarian. Start with an elaborate diagnostic workup. The veterinarian will:
- Take history and examine the symptoms.
- Check for blood glucose concentration.
- Alter the diet to some extent.
- Order Insulin or similar medication.
Daily duties include:
- Keeping blood glucose levels at home.
- Insulin injections when required.
- Diet and exercise compliance of instructions.
Maintaining progress checks:
- Report back on treatment progress monthly.
- Treat according to results and change the treatment plan as necessary.
Effective treatment depends on the regular feedback received from the patient’s veterinarian.
Administering Insulin: What Are Tips and Techniques
Presented below are essential tips and techniques that are considered necessary for properly handling insulin in a Pug with Diabetes. To begin with, one must:
- Consult a Veterinarian: Obtain a wise vet answering the query stating how much and what essence is needed concerning the Pug’s case.
- Choose the Right Equipment:
- Insulin syringes
- Alcohol swabs
- Sharps disposal container
- Establish a Routine: With regard to insulin administration, the recommendation is to carry it out once within the twenty-four hours and at the same time each such day so as to stabilize the blood sugar levels of the target subject.
- Prepare the Injection Site:
- Use an alcohol swab to clean the site of injection
- Common areas include the scruff area, and flank areas
The Role of Diet in Managing Pug Diabetes
It is evident that dietary intervention is unavoidable if one wishes to successfully manage pug diabetes. After examining, clinicians usually endorse that it is important for the diet to be high in fiber and low in fats so as to control blood sugar levels.
- High-Quality Protein: Skinless chicken or turkey and fish are recommended.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Brown rice or sweet potatoes will help release glucose later.
- Avoid Sugary Treats: Eradicate high sugar foods and drinks to evade sudden rises of blood sugar levels.
- Consistent Meal Times: Provide food to pugs at regular intervals so as to control glucose levels.
Proper dietary management is key to any diabetic pug’s health.
Exercise and Activity: Keeping Your Pug Fit
Due to the amount of energy used, it is important for pugs who are diabetic to maintain a good weight. There is need to incorporate regular physical activities for the pug and some of them include: Aim for:
- Daily Walks: Up to half an hour per day of fast walking.
- Interactive Play: Encourage the pug to move via rest using toys.
- Mental Stimulation: Use of ideas that puzzle to play with treat balls and the like.
- Scheduled Exercise: This entails limiting the time span within which exercise will take place.
“Working out usually helps in blood sugar management and all around wellbeing.”
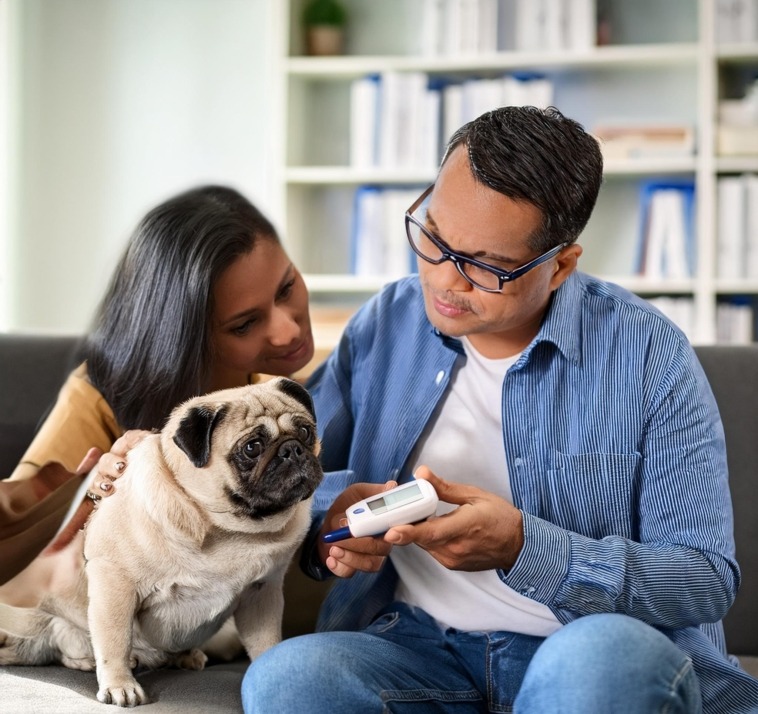
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels: Tools and Techniques
Without a precision in blockage glucose computation, it would be hard managing diabetic pugs effectively. Two or more tools and techniques usually are vital for correct estimates or timely adjustments of diabetic treatment:
- Glucose Meters: They are handheld devices which measures blood glucose concentration obtained from the prick blood samples usually taken from the paw pad of the pug.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Wearable devices that help avoid constant pricking of fingers routine by providing current blood glucose readings within the skin of the pug.
- Urine test strips: Although not very precise, these provide a secondary way of testing for the presence of glucose in the urine.
Frequent monitoring lowers the risk of negative health impact.

Learning to Tackle Emergencies: Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is defined as an abnormal decrease in blood glucose level and is a serious illness that can even be fatal. The more obvious are the symptoms:
- Tiredness
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Convulsions
Quick action plans include the following:
- Ensure the patient is given a rapidly fermented carbohydrates such as honey or a glucose jelly.
- A blood test for glucose should be performed again.
- Get in touch with the vet for assessment and management.
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a critical condition in which blood sugar levels exceed normal and may have dire consequences if not addressed. The symptoms include:
- Dry mouth
- Too much urination
- Decreased appetite
- Constant weakness
Basic steps to take include:
- Check blood sugar.
- Give the advised insulin.
- Call your vet for other necessary direction.
Out of Many Ways To Manage This Condition: Scheduled Return And Monitor
Pug diabetes is a condition which when diagnosed needs veterinary management at all times to prevent any adverse complications.
- Veterinary Visits: Schedule preventive health care visits every three to six months for complete routine preventive health care visits.
- Home Blood Glucose Monitoring: It is helpful to keep a glucometer at home and make glucose tests periodically.
- A1C Tests: To evaluate the practicability of this period, individuals should be encouraged to conduct A1C tests every six months or so and evaluate the measure during this time frame.
- Weight Management: Closely observe any increase in body weight, with the aim of avoiding obesity, a condition that makes it difficult to control diabetes..
Adhering to these practices will help manage pug diabetes well.
Support Systems: Family, Vet and Pug Communities
For proper management of pug diabetes, there is a need to have some support systems in place:
- Family Support: Family members may be of help by following the nutritious menu and exercise plans, getting glucose readings done, and emotional support.
- Pug Communities: While online support for rehab is useful, real life pug owner resources may have more value in sharing actual experiences, tips, and assist in offline struggles. These communities help expose such individuals to an environment full of growth and learning.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Management of diabetes in dogs has several challenging missing pieces of puzzle which are encountered by the responsible person, that is, the owner. To illustrate, blood sugar levels should be taken frequently, if not all the time, especially when such an animal is symptomatic.
What is more, it is very important to stick to certain habits or diet to keep the blood sugar of the canine under control. Additionally, periodically reaching out to the vet is necessary in order to change the current course of treatment if it proves ineffective.
All in all, if the sugar levels of the canine are properly and timely managed there is high likelihood that the health of the dog will improve.
- Blood Glucose Measurement: There is need to routinely check blood sugar level to ensure that so blood level should not rid to the extreme end. Use pet glucose meters that are sting resistant to counters.
- Diet and Nutrition: Eats routinely and make sure to keep all minerals and vitamins to the required levels. Also small snacks with lots of carbs must be avoided.
- Exercise: Aiding in maintaining normal weight and blood sugar levels is taking walks every day.
- Medication Adherence: Insulin needs to be administered as prescribed without missing doses.
Success Stories: The Experiences of the Administrators of Diabetes in Pugs
Most Pug owners have been able to successfully take control of Diabetes as they managed to take care of their pets. Their life stories are useful as follows:
- Mark from California: Stuck to fixed feeding times and checked the blood glucose level every day.
- Angela and Paul in New York: Regular examinations of their pug Toby by the veterinarian and physical activity was scheduled as part of his health plan.
These anecdotes depict the right ways and measures necessary for relief from pug diabetes.
The Other Aspects of Life with Managing Pug
Diabetes management for a pug extends beyond physical needs. Their health does not only depend on physical health – mental and emotional health is just as vital. Stress is one of the factors that may cause a spike in blood glucose levels. This makes the management of diabetes to be more difficult.
- Behavior change monitoring: Edit and retain any signs of change in behavior or mood as they could be signs of distress or illness.
- Comforting: Bring down the level of anxiety by providing comfort.
- Interaction: Allocate some of your time for play and show some affection.
Adopting these measures will definitely improve the quality of life of a diabetic pug.
Further Development Directions in Canine Diabetes Managing Pug
New technologies and studies make new promises for the treatment of diabetes in dogs.
- CGM, or Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Devices that can be worn will be made to give detailed measurement of blood sugar within the body.
- Insulin Devices: Accurate dispensing of insulin with control can be achieved using hands-free controlled devices.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Study seeks to harness regenerative medicine to repair or reinvent lost pancreatic cells.
They still remain optimistic in the search of different treatment methods regarding for example morphine.
Explored By: Dr. Ali Ahmad (Behavior Researcher)